Fungal skin diseases (dermatomycosis) are the most common skin diseases. Fungi have been known since ancient times; they are a special type of microorganism that combines the traits of both plants and animals, and fungi feed on organic substances. They are tenacious, able to form spores and persist in the environment for a long time, grow very slowly. Therefore, fungal diseases can proceed without manifestations for a long time, and their detection is not an easy task for doctors.
Predominantly dermatophyte fungi are causative agents of superficial fungal diseases, in particular, such as microsporia, trichophytosis (ringworm), epidermophytosis. They constantly inhabit the skin and hair of humans and animals, some in the soil. Human contact with fungi occurs. However, the skin is normally a powerful protective barrier and prevents fungi from developing pathogenic properties.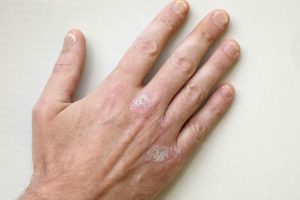
The following factors contribute to the development of fungal skin diseases:
mechanical damage to the protective barrier of the skin: cracks, microtrauma, including those obtained as a result of cosmetic procedures.
non-observance of the rules of personal hygiene at home and when visiting public saunas and baths, fitness rooms, if individual towels, slippers, hats are not used.
These factors are not leading, the skin will not allow the enemy to penetrate if the immune system is working well. A decrease in local and general immunity of the body is a decisive trigger. This is facilitated by:
Genetic causes (congenital immunodeficiencies)
Lack of vitamins and minerals
Chronic skin diseases
Endocrine diseases: diabetes mellitus in the first place, thyroid dysfunction, obesity, other hormonal problems
Long-standing chronic diseases (gastrointestinal tract, lungs, heart; tuberculosis, AIDS)
Long-term use of antibiotics, glucocorticoids, anticancer drugs.
If the fungus has overcome all the obstacles in its path, the disease develops. A feature of skin fungi is the defeat of the stratum corneum (surface) layer. Fungi feed on keratin, which is part of it. Skin, nails and hair are affected.
How do fungal skin diseases manifest?
Since only the superficial layers of the skin are involved, manifestations can be as follows:
Itchy and flaky skin without blemishes
Formation of red spots with clear edges in the form of one or multiple lesions, as a rule, accompanied by scaling and itching
Nails thicken, deformed, delaminated
Hair loss with trichophytosis
Inflammation of hair follicles with crusting and scaling
Manifestations are typical for many skin diseases. The examination data does not allow to determine whether the skin is fungal or not.
The following laboratory methods are used to establish the diagnosis:
Microscopic examination of the skin, nail plates and hair for the presence of pathogenic fungi (lead time 2 days)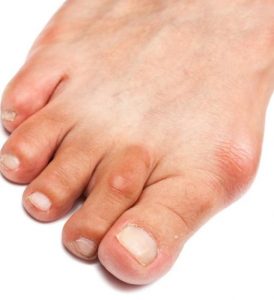
An important point for the correctness of the study is to take material at the border of healthy and affected tissues, where the probability of detecting active growth of fungi is higher. The microscopic method allows you to see a pathological fungus under a microscope or exclude its presence, but does not allow you to determine the type of pathogen. Identification of the mycelium of the fungus is a criterion for confirming active mycosis. The presence of only a dispute requires detailed study and confirmation by other methods.
Sowing on fungi (pathogens of mycoses) (up to 30 days) is a more accurate study. Skin scrapings, nails and hair are placed in special media enriched with nutrients specifically for skin fungus. The doctor observes the growth of fungi for up to a month, since they grow very slowly and it is this period that allows an adequate study to be carried out and not to miss the disease. Thanks to the sowing, the specific type of dermatophyte fungi is determined, which makes it possible to prescribe the correct antifungal drug.
Please note that the Malasezia furfur fungus, the causative agent of dandruff in animals and humans, does not grow in crops. This is his peculiarity!
In case of fungal diseases https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pathogenic_fungus, the determination of sensitivity to antifungal drugs is carried out only for a scientific purpose in order to introduce a new drug, since this is a long, laborious process and it is inappropriate in medical practice. The fact is that well-known antifungal drugs affect certain types of fungi and the doctor, upon confirmation of a fungal disease, will not wait for the further progression of the process for another month, but will prescribe a drug depending on the type of fungus determined as a result of the analysis.
How to properly prepare for research?
Skin scrapings are performed only by a doctor. Hair and nails are allowed to be collected independently and placed in a special container, if possible on the border of healthy and affected tissues. The study is carried out before the start of taking antifungal drugs or 2 weeks after the end.