Prostate cancer is one of the most common tumors in men after lung cancer. Early recognition has a great chance of a complete cure. For this purpose, the prostate-specific antigen, PSA, has long been used as a tumor marker. It is called specific because it is accurate for examining the prostate gland, but it is not accurate enough for detecting malignant tumors, because may increase with a number of other prostate diseases. The Prostate Health Index – PHI, is recognized by the international cancer community as the most reliable indicator among tumor markers at the moment.
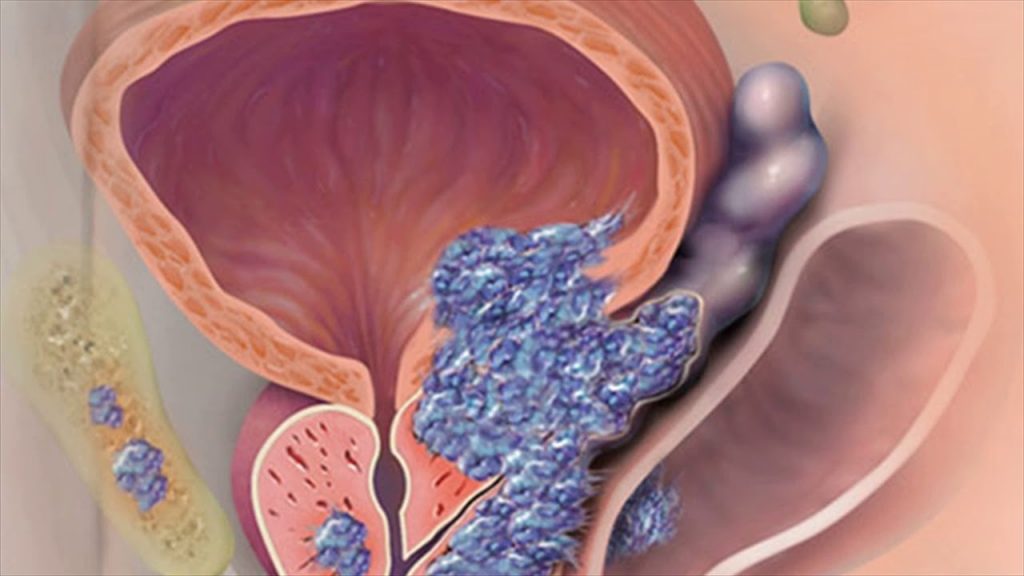
Let’s get it clear right away. The only recognized and accurate method for diagnosing cancer is histological examination – examination of prostate tissue obtained by biopsy. Biopsy is an invasive procedure, it is performed strictly according to indications and can cause complications: bleeding, inflammation, pain, problems with urination. PSA and PHI allow you to select the category of people who really need a biopsy.
Prostate. How does it change with age?
The prostate is a small chestnut-shaped gland located under the bladder and in front of the rectum. The function of the prostate is very important – it produces PSA, which is necessary for sperm thinning and sperm motility. With age, the tissue of the gland begins to grow, and every second man develops an adenoma, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). There is a risk of degeneration into malignant cells.
How to suspect a tumor?
The initial stages of the disease often do not manifest themselves in any way, and the patient is not alert to consult a doctor in a timely manner. “Alarming signs” are problems with urination, when the tissues of the prostate squeeze the urethra at the exit from the bladder: with strong urges, the stream is sluggish and there is little urine, and therefore frequent night trips to the toilet. There are problems with erection, intercourse is accompanied by pain, blood in the urine is possible. It is not uncommon for a man to turn to other specialists with complaints of pain in the spine, ribs and pelvic bones, missing the primary signs – this may be a manifestation of advanced stages when the tumor spreads throughout the body, giving metastases.
Hence the conclusion suggests itself: there is no need to wait. It is recommended to be examined for PSA annually for every man over 40 years old. Other risk factors are also taken into account: familial cases of prostate cancer, obesity, smoking, alcohol abuse.
What is PSA testing for?
PSA is used as a tumor marker; its high level is associated with the development of cancer. Tumor cells disrupt the structure of the prostate gland, as a result of which PSA enters the general bloodstream. But sometimes PSA “leak” can occur in benign conditions. Total PSA is the sum of all forms of PSA, and normally does not exceed 4 ng / ml. Values up to 10 ng / ml are possible in benign pathology (BPH). A PSA level above 10 ng / ml indicates a high risk of cancer and is an indication for biopsy.
Total PSA is not a specific sign of oncology; values from 2 to 10 ng / ml can be detected both in benign changes and in a malignant tumor.
Moreover, an increase in PSA levels is possible with inflammation of the prostate, trauma and other effects on the organ.
What is PHI and what is its advantage over general PSA?
PHI – Prostate Health Index – a test that determines the level of total PSA, the percentage of free PSA, – 2proPSA and calculates indicators that accurately indicate the risk of developing cancer. This is possible due to the fact that scientists have found and isolated the form – 2proPSA. It is produced by malignant cells of an aggressive tumor, and at an early stage may not affect the level of total PSA.
International research has highlighted a number of benefits of PHI:
Improves the detection of prostate cancer, especially with a PSA level of 2-10 ng / ml
Reduces unnecessary biopsies – a rather traumatic procedure
Increases the likelihood of detecting aggressive forms of cancer that require active treatment
During the initial examination, it makes it possible to more accurately identify patients in the category of high risk of developing cancer.
Who is the PHI study for?
With a total PSA level of 2 to 10 ng / ml
If a prostate tumor is suspected on digital examination and ultrasound data
If there are “warning signs”
Follow-up of patients with established prostate cancer during or after anticancer treatment for early detection of tumor progression
Preventive examination of men over 40 years old
How to decipher the result?
A PHI of less than 25 indicates a low risk of cancer. Retesting for PSA and PHI is recommended after one year.
A PHI greater than 25 indicates a high risk of prostate cancer https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate_cancer and requires a biopsy.
How to properly prepare for the study?
Given that PSA may increase after exposure to the prostate, the study should be carried out no earlier than:
One month after prostate biopsy and cystoscopy
10 days after transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and prostate massage
Abstain from intercourse per day
You can donate venous blood during the day, 3 hours after eating.
Remember! Timely examination allows you to detect cancer at an early stage, when a complete cure is possible.