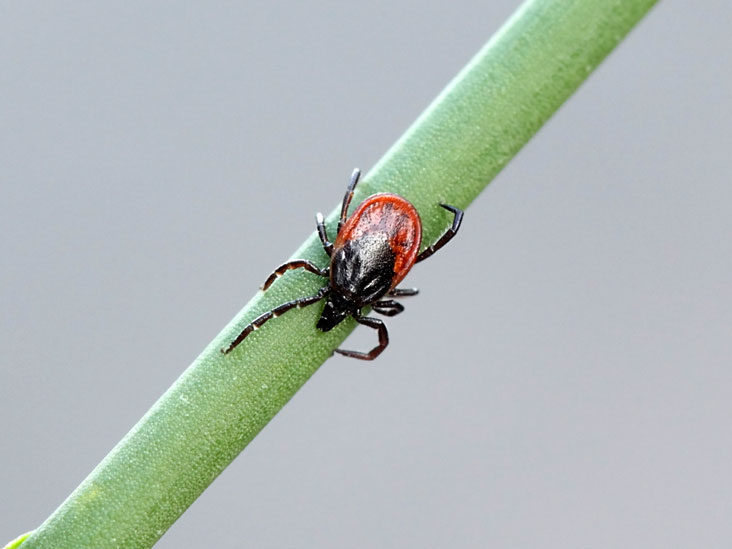
Fact 1. You can only catch borreliosis from a tick bite
The disease is not spread from person to person, or from animals to person. And pets can only contribute to infection by bringing ticks into the house on their fur.
Fact 2. Not all ticks are the source of infection
On the territory of Russia, about 30-60% of ticks are considered “infected”. At the same time, the risk of meeting infected insects is much higher in the endemic regions of the country: in the Urals, Altai, the Far East and Siberia. In the rest of the territory, the probability of infection is quite variable and is associated with the characteristics of the vegetation (coniferous, deciduous forest, fields, steppes, etc.) and the climate.
Fact 3. A bite is not the same as infection
Borreliosis takes 36 to 48 hours to transmit, during which time the tick must have “access” to the blood. The risk of infection increases depending on the time of tick suction. It is believed that if a tick is removed during a day on the human body, then it does not have time to transmit the pathogen
For this reason, young ticks (up to 2 mm in size), which are much more difficult to spot, pose a much greater threat than their “adult relatives”.
In addition, it is much more difficult to extract small insects “unharmed”, which means that it is often not possible to hand over such a tick for analysis.
Fact 4. Symptoms of borreliosis do not appear immediately
Borreliosis, like any other infectious disease, has a certain incubation period. In this case, it is, on average, 7 to 14 days from the bite.
However, it can be shortened up to 2-5 days (fulminant form) or lengthened up to several weeks.
At this time, the victim, as a rule, is not worried about anything, and the first symptoms appear towards the end of the “incubation” period.
Fact 5. Borreliosis can be asymptomatic
To be more precise, then – without any specific symptoms. And the manifestations of the disease are often indistinguishable from those of the flu.
Weakness, fatigue, headaches, body aches and a slight increase in temperature (up to 37.0-38.0 degrees), which appeared some time after the bite, may become the only symptoms of infection.
And you can confirm or deny an acute infectious process using a blood test for antibodies (IgM).
Fact 6. Borreliosis often causes complications
It is primarily about the “hidden” forms of the disease. When, under the guise of chronic fatigue and a cold, defeat “goes”:
heart (myocarditis, pericarditis and others),
nervous system (polyneuritis, meningitis)
and the musculoskeletal system (pain in muscles, joints and bones of a migratory nature).
Fact 7. “Target” on the skin is a sign of borreliosis
A characteristic sign of the disease is redness of the bite site, with a gradual expansion to adjacent skin areas. In this case, the center of the “spot” gradually fades, which gives the redness the shape of a “target”, reaching up to 10 cm in diameter.
By the way, for the property of “moving” on the surface of the skin, the borreliosis “target” is called “migratory or annular erythema.”
Fact 8. Infection with borreliosis can be detected years later from a bite
The chronic course of infection under the guise of other diseases is a characteristic feature of untreated borreliosis. And you can check for infection after 5 weeks or more with a blood test for class G antibodies.
Fact 9. Borreliosis https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lyme_disease is well treated with antibiotics
In this case, of course, the earlier the drug is prescribed, the higher its effectiveness. However, it is possible to reliably confirm infection with borreliosis not earlier than 2-3 weeks from the moment of the bite (when IgM antibodies appear in the blood). This means that the appointment of an antibiotic immediately after a bite can only be prophylactic.
Fact 10. There was a vaccine before 2002
However, its production was discontinued due to low demand and sufficient effectiveness of timely antibiotic therapy.