The vaccination against chickenpox, despite the promises of the Ministry of Health, is still not listed in the vaccination calendar in 2020. At the same time, the incidence in recent years has doubled, and the infection is a restriction for visiting kindergartens and schools. How long does a child’s quarantine last after an infection? And how can you make sure your child is protected during outbreaks?
How can you get infected
The incubation period of infection, that is, the time from contact with an infected person to the appearance of the first signs, is usually 14-17 days, but it can vary from 10 to 21.
A person becomes contagious about 2 days before the appearance of the first elements of the rash and within 5 days after the disappearance of the last of them.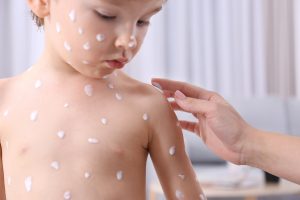
At the same time, chickenpox is transmitted by airborne droplets, has the highest “volatility” and easily spreads even between the floors of apartment buildings. So you can “catch” the infection simply by living with the “source” in the same entrance.
How does it manifest
As you know, children get sick many times more often and more easily than the adult population. And among the first symptoms of the disease – a rise in temperature to 38-39 degrees and “classic” symptoms of intoxication (weakness, loss of appetite, drowsiness, moodiness).
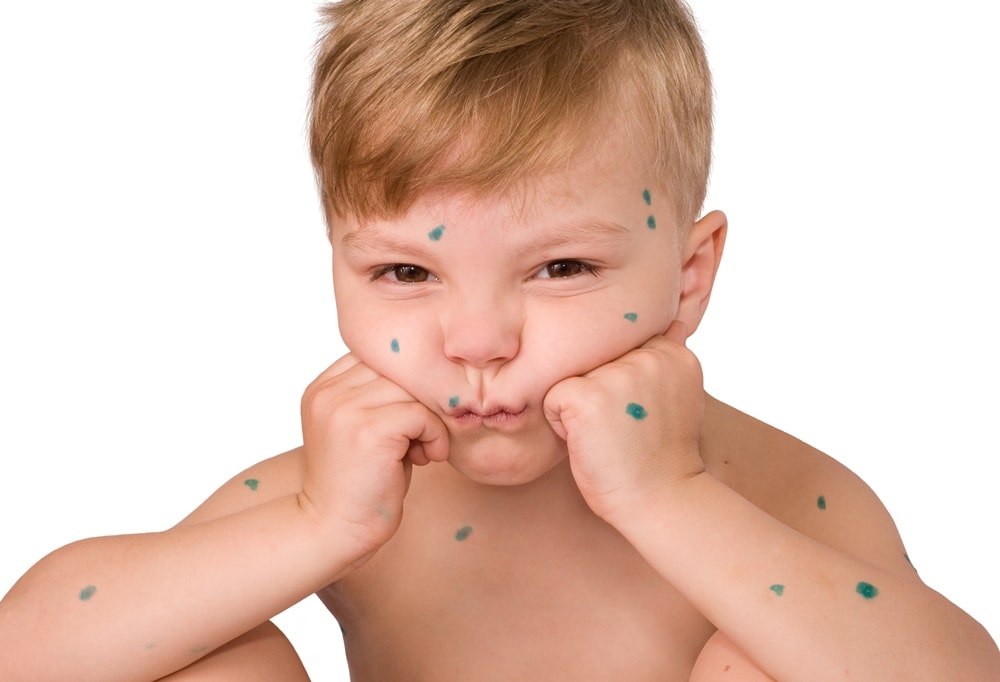
Almost simultaneously with the temperature, a characteristic rash appears on the child’s body.
The affected area is:
face,
scalp
back,
stomach,
breast,
shoulders
and hips,
small red spots appear on the skin, at first glance similar to crimson bites. Then the formations become denser and “rise (papule), turn into a bubble with transparent contents, and after 1-2 days they open and heal with a” crust “.
Each episode of “falling asleep” is accompanied by an increase in temperature. And the elements themselves are quite itchy, which often provokes scratching and the addition of a bacterial infection.
It is noteworthy that rashes do not appear on the palms and soles of chickenpox, which is a distinctive sign of infection from some other similar diseases. But on the mucous membranes of the mouth and others, you can find characteristic bubbles.
And complete recovery occurs no earlier than the 10th day from the beginning of the process.
Rare complications
In some, albeit rare, cases, chickenpox in a child can end in complications:
furunculosis,
pneumonia,
as well as encephalitis and meningitis.
True, such complications often occur in newborn or weakened children (immunodeficiency, chronic diseases, congenital defects, and others).
And it’s time to sound the alarm if:
the temperature more than 37 degrees lasts more than a week and is growing;
runny nose and cough appeared
diarrhea and vomiting joined.
How long does isolation last
After detecting a case of chickenpox, not only the infected, but also all those who are not sick or vaccinated, who are in contact with him both during the period of rashes and 2 days before them, are quarantined.
For a child, this means that he cannot visit child care facilities and crowded places for up to 10 days from the moment the last element of the rash has healed.
Non-immunized contact persons are urgently vaccinated or given anti-tetanic immunoglobulin.
The second option is primarily shown:
those who have contraindications to vaccination,
pregnant women, in the absence of protective antibodies,
newborns, if the mother is diagnosed with chickenpox 5 before and within 48 hours after childbirth,
as well as patients who have undergone bone marrow transplantation, regardless of whether they have had chickenpox before.
Those who have antibodies have nothing to be “afraid” of, so monitoring them is not provided for by sanitary standards.
How to assess the risk of infection
The only way to assess the risk of infection is a blood test for IgG antibodies to the Varicella-Zoster virus.
The study is shown to both children and adults. But it is most often used to find out the intensity of immunity to chickenpox https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chickenpox in those who do not have data on vaccinations and previous infection, or suspect that they have suffered from an atypical or asymptomatic form.